Microfluidics for high performance thermal management
Reliable high-density, high-performance, and for some applications, high-power microelectronics with an incredibly powerful, integrated cooling capacity. TNO’s High Performance Thermal Management Technology is making it possible.
Whether regarding power electronics in electric vehicles, server boards in data center racks, or 5G/6G antenna base stations, microelectronics manufacturers and suppliers are constantly challenged to improve the performance of their products. Electric-vehicle owners want longer ranges and shorter charging times, while data centers are always on the lookout for installations that will take up less valuable floor space and use less power and water but have ever increasing performance. Developers of antenna base stations seek sustainable, lightning-fast communication in ever-smaller, more efficient and maintenance free telecom infrastructures.
Hundreds of times more capacity through integrated device cooling
An important way to improve the performance of microelectronics, as well as the packages into which they are integrated, is structure size reduction, which increases the energy density of the device. Doing so requires the most efficient cooling possible. This can be through upscaling or downscaling, but usually, both go hand in hand: performance is upscaled while weight and size are downscaled, also regarding cooling.
TNO’s High Performance Thermal Management Technology is the solution to this twofold challenge. The technology offers hundreds of times more cooling capacity than conventional applications while being integrated, on a small scale, close or into the microelectronics themselves. This results in using much less space and being positioned directly on top of the heat source.
Technology for active thermal management
TNO has developed and patented the disruptive microfluidic, two-phase cooling technology, which features:
- An ultrathin cooling body, wafer level (100µm), PCB level (1 mm+)
- An extremely high (500x higher) heat-transfer coefficient (>> 250watt/cm2)
- An extremely low (>>10 times lower) flow rate
- A cooling body that can be bonded on or etched in (silicon) wafers/chips
- Manufacturing made possible by a range of cost-efficient techniques
The liquid cooling technology can be applied in numerous fields – from data centers, electric vehicles and LEDS to active thermal management of Fuel Cells.
TNO published their research in modelling two-phase flow in microchannels with heat spreading on the ASDAM conference in 2022. Efforts in modelling the effects of surface tension are published on the Ex-HFT10 conference in 2024. Furthermore, this paper also describes an experiment where the high heat flux of 250 W/cm2 is obtained while the chip interface temperature remained below 90 °C. The papers can be downloaded at the bottom of this page.
The MicroFluidic structure can also function as evaporator or boiler unit for waste heat recovery systems applied on heavy duty (Hybrid) internal combustion engines of trucks, busses, generators and ships. TNO’s paper on this topic can be downloaded in the bottom of this page.
3D tool Microchip cooling
Improving data center efficiency
One of the application areas of this new technology is in microelectronics integrated into the server boards mounted in data center server racks, contributing to an overall increase of data center efficiency and compute power.
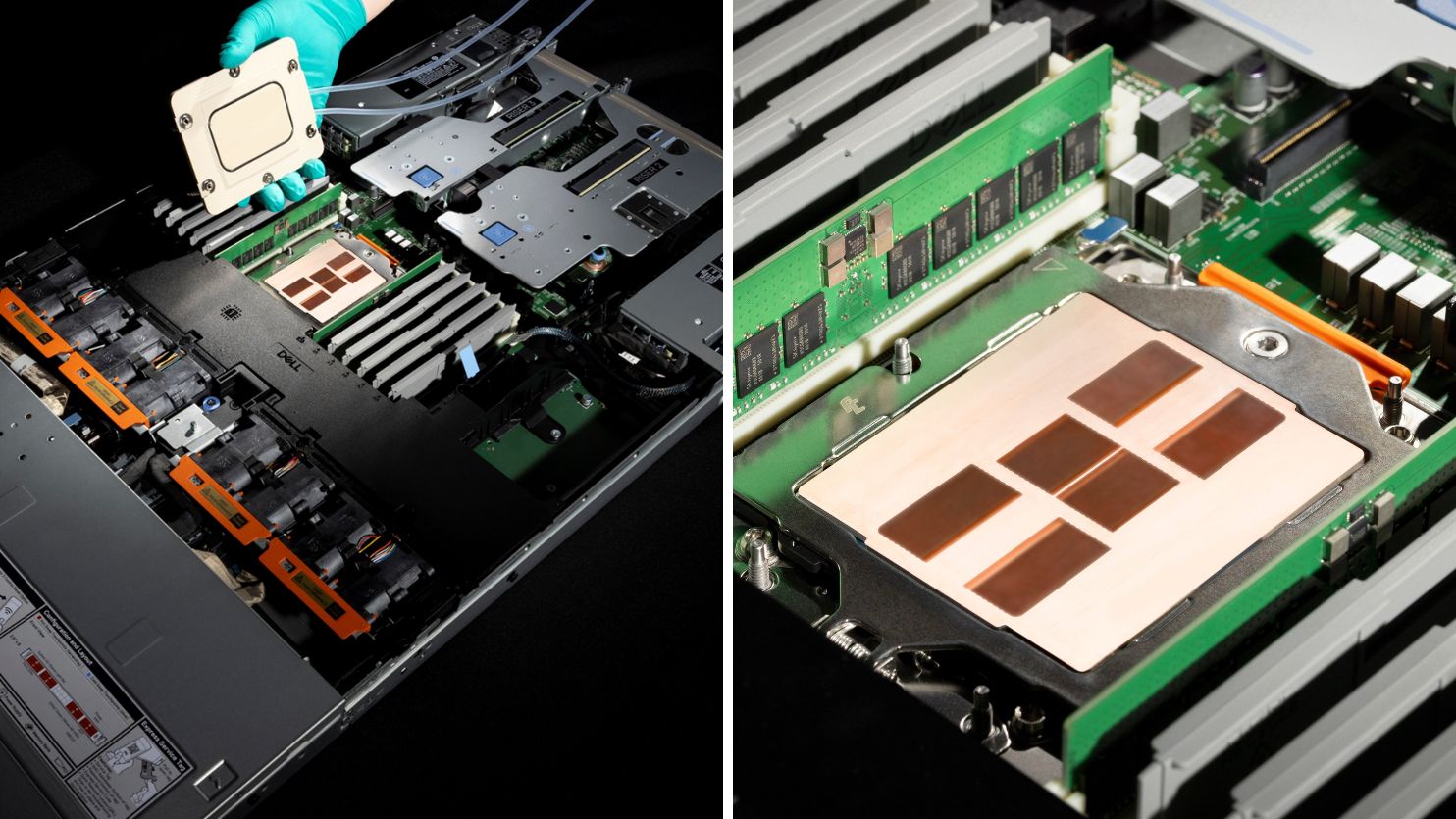
TNO IN-IHS 2-phase micro cooling
6 micro fluidic structures or vapor chambers are integrated into the metal Internal Heat Speader (IHS) of this 400Watt CPU. On top of this IHS an in- and outlet channel stack and closing lid are mounted. 4 to 6mm hoses provide the cooling liquid to and from the micro fluidic cooled chip package.
Unique features
- Extreme low 250mL/ kW flow required enabling miniaturized cost efficient cooling infrastructure;
- ø4 to 6 mm hoses, no components loss on server board;
- Low volume, closed fluid loop reducing cooling liquid TCO;
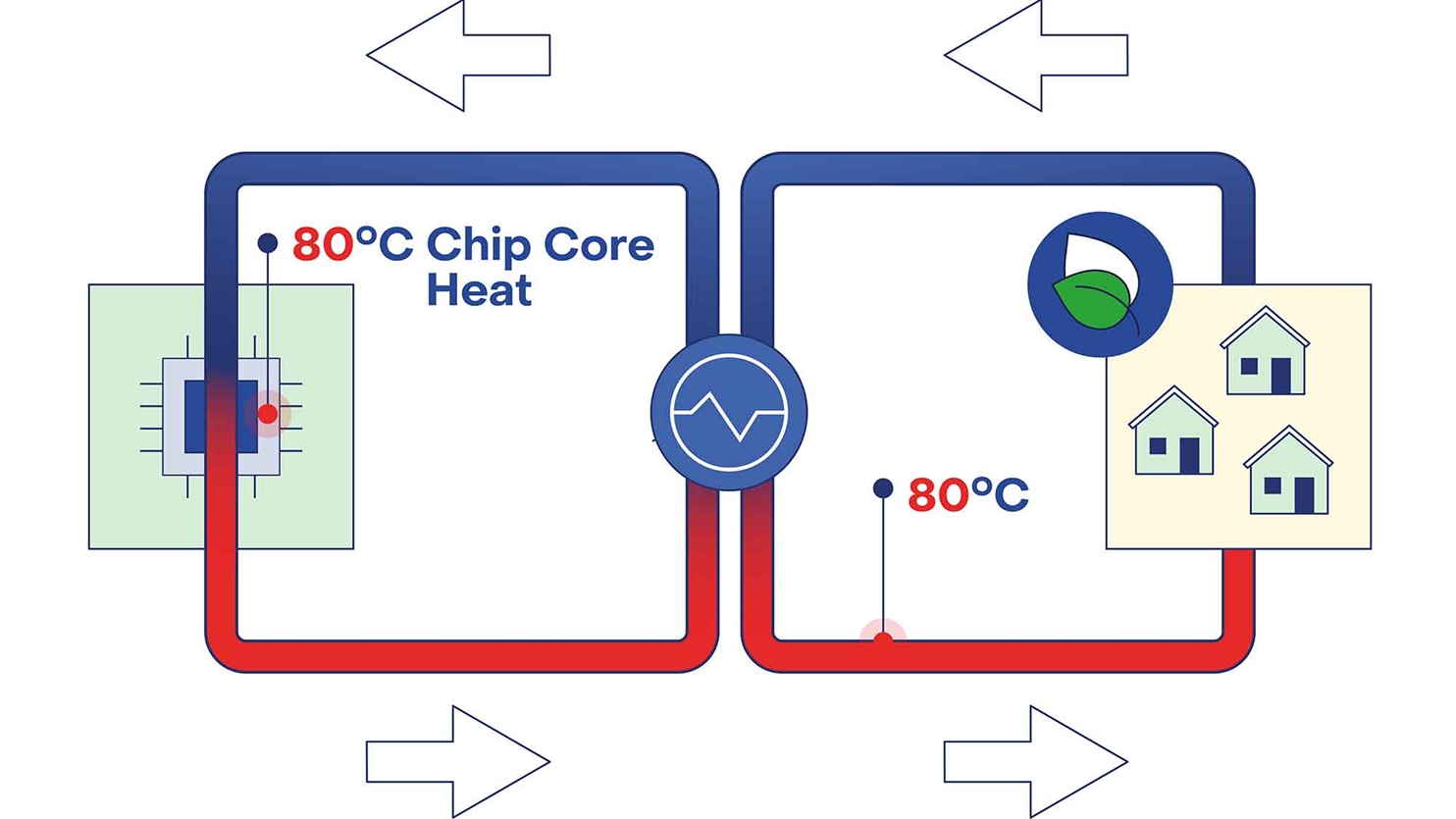
- High temperature cooling 65° in /75° out enabling high quality energy harvesting;
- Non PFAS/ Non Toxic fluid used, GWP ~1;
- Low thermal resistance of 0.045 K/W enabling efficient AI/ HPC compute;
- Lifetime increase (low ΔT over chip);
- Mass production compatibility;
- IN-CHIP 8kW xPU Micro Cooling under development (250W/cm2)
- High quality “waste” energy can be applied to heat nearby offices, industry and/ or homes reducing global energy consumption and possibly increase the acceptance for local governments and residents for new data center buildings
Cooling application in electric vehicles (EV's)
A second application area concerns the power electronics integrated into electric cars, so-called EV power electronics. These include inverters, on-board chargers (OBC), electric motors, battery packs and battery cells/stacks.
TNO’s microfluidic, two-phase cooling technology enables a higher range and shorter charging time by means of:
- In-situ, small-scale inverter cooling
- Microchannel-cooled electric motors
- Small-scale, highly efficient, built-in charging systems
- Lightweight battery pack systems with optimal direct to battery or in battery cooling characteristics
- Integration options for all cooling circuits

Application in high density microelectronics
A third application area is that of high-density, high-complexity, and in some applications, high-power microelectronics on interconnected printed circuit boards (High density PCBs). TNO’s microfluidic, two-phase cooling technology enables:
- In-package (PCB-level) microfluidic cooling
- Double-sided microfluidic device cooling within packages
- Hotspot prevention of devices at high temperatures
Cooling application in 5G/6G antenna base stations
Manufacturers of antenna base stations are faced with an ever-increasing need for cooling, as the microelectronics density and complexity in antenna modules continues to increase. At present, passive cooling is typically used via air cooling fins on the antenna chip array. Microfluidic, two-phase cooling technology is making active antenna integrated cooling an option by using a closed-loop, two-phase solution which also increases the overall performance.
Thanks to greatly improved cooling, manufacturers can build more compact antenna base stations, which are easier to install and are less visually polluting of urban and natural landscapes. Their compactness also opens up new integration possibilities, in lampposts, for example.

What can TNO offer?
- Ultimate thermal fluidic design for demanding applications
- Employing advanced modelling & thermal/ flow experience
- Development of ultimate manufacturing method (AM / Conventional)
- Validation of the concept by lab experiments & Execution runs
- Support to your R&D team (system engineering, control engineering, process intensification) for complex projects
- IP license for your field of use
Would you like to know more or get involved?
Are you active in the telecom, semiconductor, automotive, or another industry faced with cooling challenges? Would you like to know more about TNO’s High Performance Thermal Management Technology and find out what value it has for you? Get in touch with Patrique Boerboom.


