Digitalising and smarter production in the manufacturing industry
By fully embracing smart manufacturing, the Dutch manufacturing industry can make an impressive leap in the coming years and be a major forerunner within Europe by 2030. Ambitious? Certainly. At TNO, we’re convinced that the Dutch manufacturing industry has what it takes to make the necessary digitalisation leap in the coming years.
The power of smart manufacturing
Unprecedentedly speed and efficiency in product design, production, and delivery – this is the power that digitalisation brings to the manufacturing industry. And it doesn’t stop there. Smart manufacturing can also ensure that the manufacturing industry responds more quickly to societal challenges, such as the need for more sustainable production methods and the ability to adapt to individual client requirements – even in mass production – to better match supply with demand. In these times of geopolitical tension, the transition to smart manufacturing can also significantly contribute to Europe’s quest for greater strategic autonomy.
The technology is only part of the story
There is still a lot to be done. For instance, there is still a lack of consistent, long-term R&D programmes that focus not only on client demand, but also on the common problems faced by manufacturing companies as they make the digitalisation transition. In doing so, it is worth remembering that it is not enough to only focus on the technical side of things. Digitalisation requires not only a cultural change, but also major organisational adjustments and process optimisation. This immediately explains why, despite the availability of advanced technological solutions, it is still a big challenge to realise the ambitions of smart manufacturing.
Transformations
In addition to digitalisation, production technologies and networks are also essential. Eight transitions play an important role in this. This is shown schematically in the Smart Industry Wheel, the Dutch elaboration of Industry 4.0 and 5.0. These eight transformations are the starting point for the National Action Agenda, which will help manufacturing companies, ICT companies, and public authorities to collaborate with a clear focus and coherence.
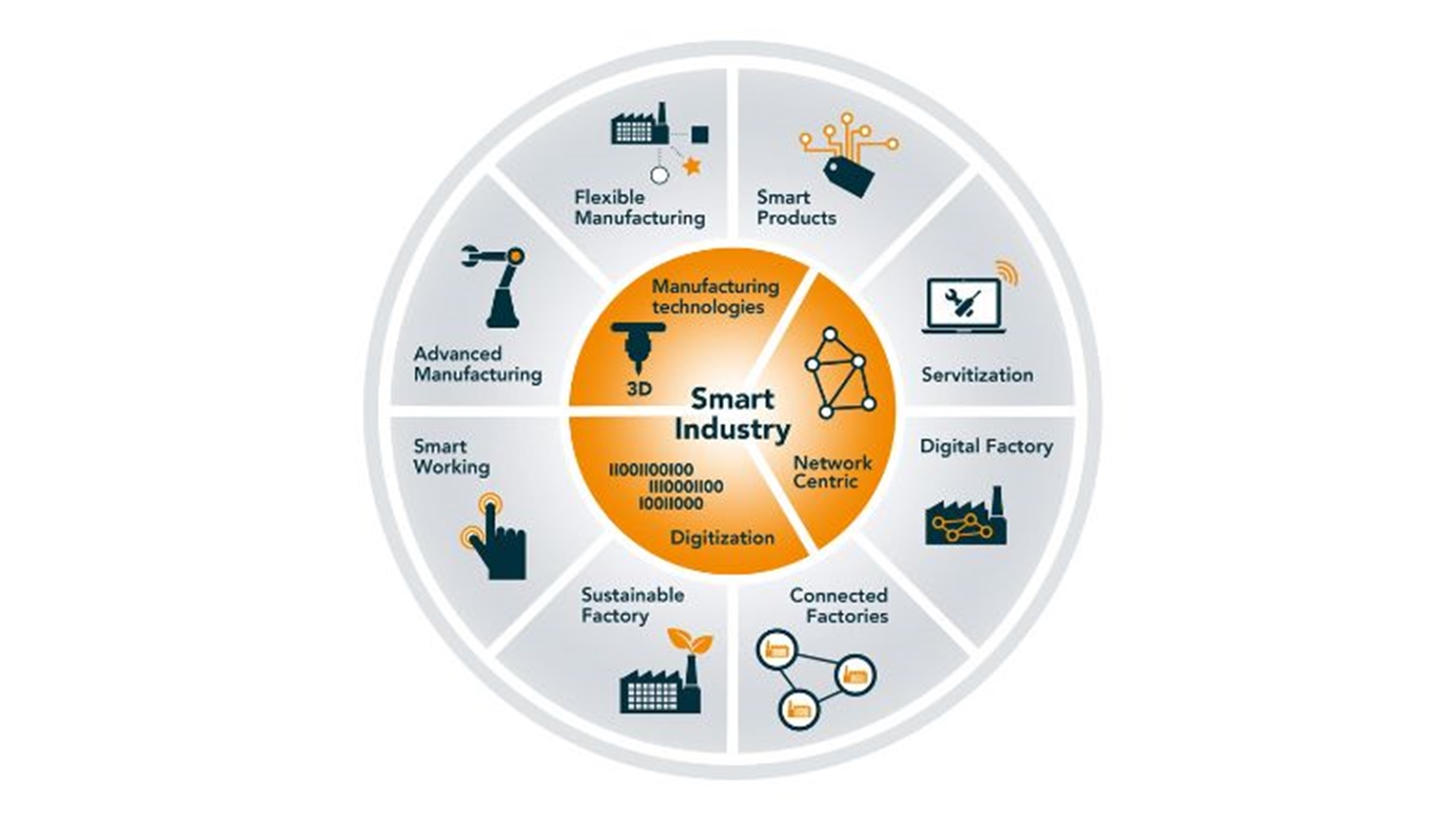
The 8 key transformations for Smart Industry described in a the Smart Industry wheel consisting of: Flexible Manufacturing, Smart Products, Servitization, Digital Factory, Connected Factories, Sustainable Factory, Smart Working & Advances Manufacturing.

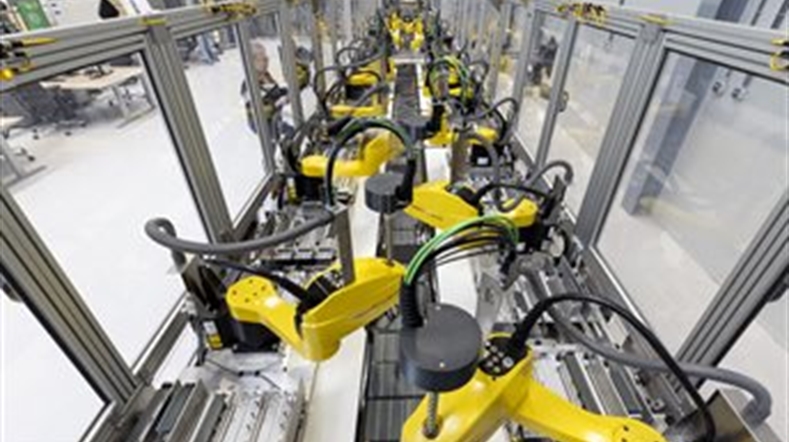
Manufacturing throughput and quality
Focus on hyper efficiency, zero-defect, first-time-right production.
Solutions to make robots, sensors, and production machines work together flawlessly and autonomously adapt to changing production flows. Flexible and competitive production thanks to the power of robotisation and automation.
Manufacturing variability
Harnessing the potential of robotisation and digitalisation to produce a specific part at a cost more in line with mass production.


Value chain integration
Automation of the entire production process and digital collaboration with suppliers, service providers, and customers. Tools for manufacturing companies for a digital and autonomous production environment.
Approach
TNO is developing applicable knowledge and uniting partial solutions into integral solutions that will take your manufacturing company forward. Collaboration is self-evident. From our independent role, we bring all stakeholders together. Everyone works from their own expertise, allowing their knowledge and skills to be used optimally. We innovate mostly in fieldlabs and our own research facilities. Together with our partners, we devise, develop, and test solutions to challenges in smart manufacturing there. This helps us gain an impression of their practicality and consistently helps us to make the state-of-the-art possibilities tangible and applicable. In the field of smart manufacturing, we work closely with the Smart Industry Programme Office and Holland High Tech and, as TNO, we have a good overview and independent opinion on the latest state-of-the-art technology, available test facilities, integrator parties and cost-benefit analyses of the investments to be made in digitalisation, sensors, automation and robotics. We use a ‘test before invest’ approach, combined with short-cycle innovation, to minimise business investment risk, accelerate innovation, and increase the likelihood of success. Read more on the TNO Fast Track website.
Smart Industry impact: looking back and forward
Want to know more? Read the whitepaper on on the impact of the digitalization of the manufacturing sector in the Netherlands with a special focus on SMEs.
Workfield Smart Manufacturing
| Production challenges | Research goal | Research topics | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Manufacturing throughput & quality |
Hyper efficient, smart manufacturing, zero defect manufacturing, first time right |
Throughput
Product quality:
System/ equipment quality:
|
| 2. | Manufacturing variability | High-mix low volume, high complexity |
Variability & flexibility:
|
| 3. | Digitalisation & value chain integration | Digitalisation, ecosystem assembly, transparency & consistency |
Digitalisation:
Value chain integration:
|
Our latest developments
Partnering for mutual progress


TNO spin-off Scenexus secures 1.6 million euro investment


Scale up: manufacturing throughput and quality


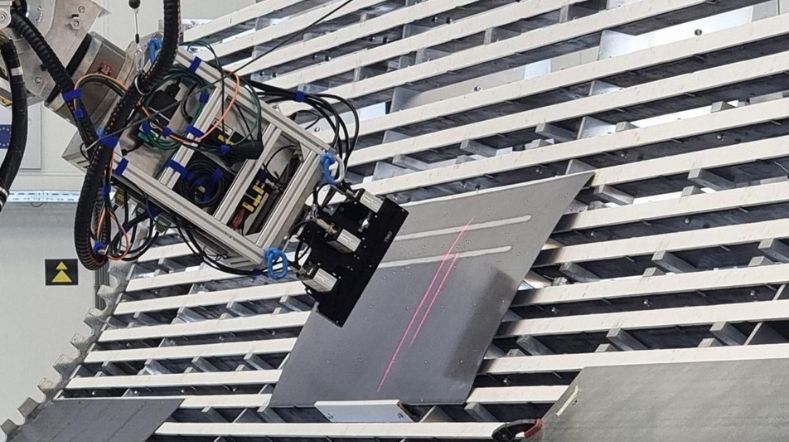
Non-destructive inspection


Strategic autonomy: digitalisation and value chain integration






