Airbus and TNO to develop aircraft laser communication terminal
Airbus and the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research (TNO) have launched a programme to develop a laser communication terminal demonstrator for aircraft, known as UltraAir.
The project, which is co-financed by Airbus, TNO and the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), is part of the European Space Agency’s (ESA) ScyLight (Secure and Laser communication technology) programme. It covers the design, construction and testing of the technology demonstrator. Laser communication technologies are the next revolution in satellite communications (satcom), bringing unprecedented transmission rates, data security and resilience to meet commercial needs in the next decade.
High-speed data connections
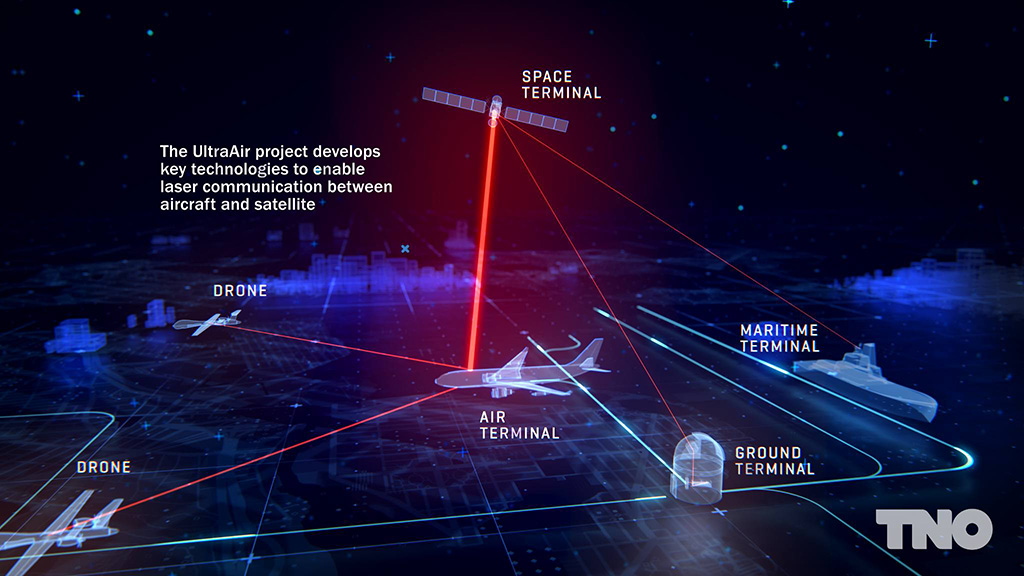
The UltraAir terminal will be capable of laser connections between an aircraft and a satellite in geostationary orbit 36,000 km above the Earth, with unparalleled technology including a highly stable and precise optical mechatronic system. The technology demonstrator will pave the way for a future UltraAir product with which data transmission rates could reach several gigabits-per-second while providing anti-jamming and low probability of interception.
In this way UltraAir will not only enable military aircraft and UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) to connect within a combat cloud, but also in the longer term allow airline passengers to establish high-speed data connections thanks to the Airbus’ SpaceDataHighway constellation. From their position in geostationary orbit, the SpaceDataHighway (EDRS) satellites relay data collected by observation satellites to Earth in near-real-time, a process that would normally take several hours.
Project group and expertise
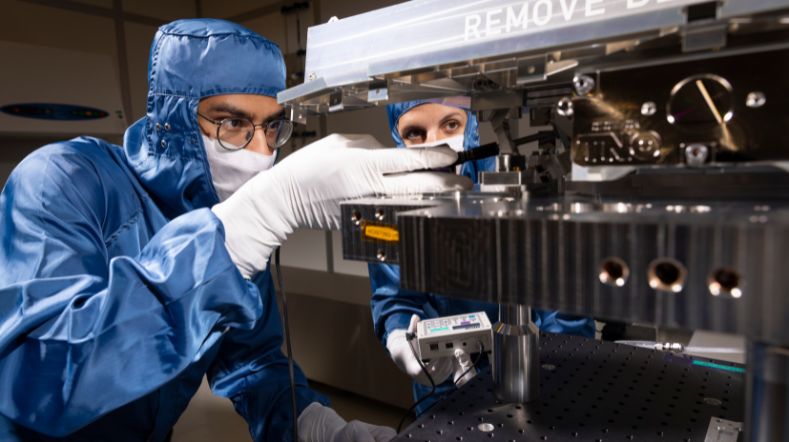
Airbus is leading the project and brings its unique expertise in laser satellite communications, developed with the SpaceDataHighway programme. It will coordinate the development of the terminal and testing on the ground and in the air. As key partner of the project, TNO provides its experience in high-precision opto-mechatronics, supported by the Dutch high-tech and space industry. Airbus Defence and Space in the Netherlands will be responsible for the industrial production of the terminals. Airbus’ subsidiary Tesat brings its technical expertise in laser communication systems and will be involved in all testing activities.
Planned tests
The first tests will take place at the end of 2021 in laboratory conditions at Tesat. In a second phase, ground tests will start early 2022 in Tenerife (Spain), where connectivity will be established between an UltraAir demonstrator and the laser terminal embarked on the Alphasat satellite using the ESA Optical Ground Station. For the final verification, the UltraAir demonstrator will be integrated on an aircraft for flight testing by mid-2022.
As satellite services demand is growing, the traditional satcom radio-frequency bands are experiencing bottlenecks. Laser links also have the benefit of avoiding interference and detection, as in comparison to the already-crowded radio frequencies, laser communication is extremely difficult to intercept due to a much narrower beam. Thus, laser terminals can be lighter, consume less power and offer even better security than radio.
This new programme is a key milestone in the roadmap of Airbus’ overall strategy to drive laser communications further, which will bring forward the benefits of this technology as a key differentiator for providing Multi-Domain collaboration for Government and defence customers.
Get inspired
Optics


Time setter story: Max van Strien


TNO technology selected for Secondary Mirror of W. M. Keck Observatory


Time setter story: Benjamin Brenny


Space systems engineering


